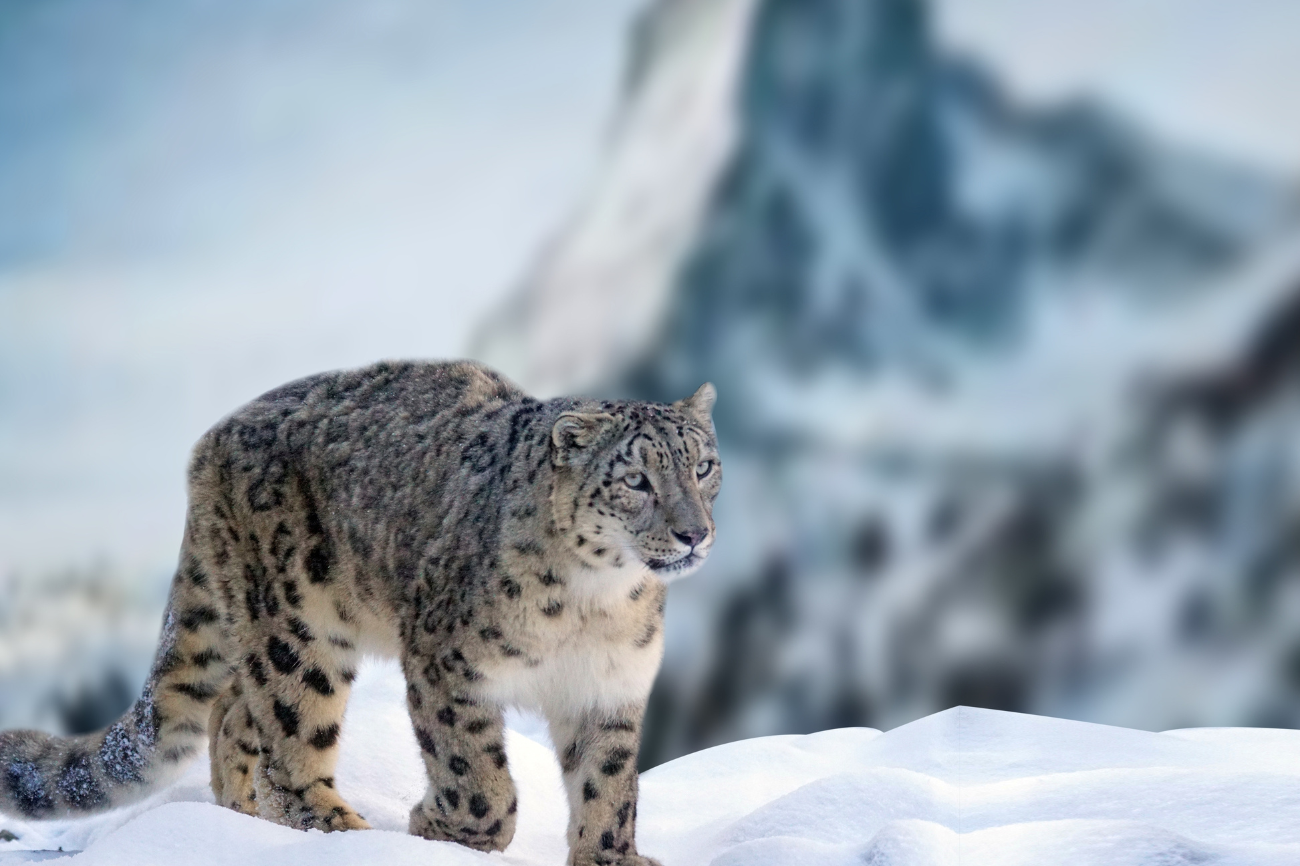
When it comes to the majestic creatures of the wild, the Snow Leopard stands out with its stunning appearance and elusive nature. Often referred to as the “ghost of the mountains,” the Snow Leopard roams the rugged terrains of the Himalayas and Central Asia, embodying a mysterious and captivating essence. Let’s dive into the world of this beautiful yet endangered species and uncover the secrets of its survival in some of the world’s harshest environments.
Habitat and Range
The Snow Leopard is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia, including the Himalayas, the Karakoram, and the Hindu Kush. It thrives in alpine and subalpine zones at elevations ranging from 3,000 to 4,500 meters (9,800 to 14,800 feet). These felines are well-adapted to the cold, arid environments where they live, thanks to their thick fur, long tails, and powerful limbs. Their expansive range covers twelve countries, including China, Mongolia, India, and Nepal.
Physical Characteristics
Snow Leopards are medium-sized big cats, with males weighing between 90 to 120 pounds and females typically being smaller. They have a thick, soft coat of fur that is grey or smoky-grey with black rosettes and spots, providing excellent camouflage against the rocky terrain. Their short, stocky limbs and large paws act like snowshoes, distributing their weight evenly as they traverse the snow. Their long, bushy tails, which can measure up to 40 inches, help them maintain balance and protect them from the cold when curled around their bodies.
Diet and Hunting
Snow Leopards are carnivores with a diet that primarily consists of blue sheep (bharal), Himalayan tahr, and other mountain ungulates. They are opportunistic hunters and will also prey on smaller animals like marmots, hares, and birds. Known for their incredible strength, Snow Leopards can take down prey three times their own weight. Their hunting technique involves stalking their prey from above, using the terrain to their advantage, and then leaping down to deliver a powerful bite to the neck.
Behavior and Reproduction
Snow Leopards are solitary animals, coming together only during the breeding season. They communicate through scent markings, vocalizations, and scrape marks on the ground. Their mating season occurs between January and March, with a gestation period of around 90 to 100 days. Females give birth to litters of 1 to 5 cubs in well-hidden dens lined with their fur. Cubs are born blind and helpless, relying on their mother for warmth and nutrition. They begin to explore outside the den at around two months old and stay with their mother until they are about 18 to 22 months old.
Conservation Status
The Snow Leopard is currently listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, with an estimated population of 4,000 to 6,500 individuals in the wild. Their numbers are threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. The Snow Leopard’s beautiful fur makes it a target for illegal hunting, and its bones are used in traditional medicine. Additionally, as their natural prey becomes scarce due to hunting by humans, Snow Leopards are forced to prey on livestock, leading to retaliation from local herders.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to protect the Snow Leopard involve a combination of scientific research, community engagement, and policy advocacy. Organizations like the Snow Leopard Trust and the Snow Leopard Conservancy work tirelessly to monitor populations, protect habitats, and reduce human-wildlife conflict. Conservation strategies include creating protected areas, implementing livestock insurance programs to compensate herders, and promoting sustainable livelihood initiatives that reduce dependency on livestock.
The Importance of Snow Leopards
Snow Leopards play a crucial role in maintaining the health of their mountainous ecosystems. As apex predators, they help regulate the populations of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and ensuring the stability of the vegetation. This balance is vital for the overall biodiversity of the region, impacting everything from the smallest plants to the largest herbivores.
How You Can Help
You can contribute to Snow Leopard conservation by supporting organizations dedicated to their protection, spreading awareness about their plight, and advocating for stronger wildlife protection laws. Responsible tourism that respects wildlife habitats and supports local communities can also play a significant role in conservation efforts.
Final Thoughts
The Snow Leopard is a symbol of the wild beauty and fragility of our planet’s high-altitude ecosystems. Protecting this enigmatic creature requires global cooperation and a commitment to preserving the natural world. By learning about and supporting Snow Leopard conservation, we can help ensure that these magnificent animals continue to roam the snowy peaks for generations to come.






What do you think?
Show comments / Leave a comment